STEEL WIRE ROPE. CORD. CONTROL CABLE. CONDUCTIVE CABLE
Steel wire rope, cord, control cable, conductive cable

Standard request must contain the list of data which will allow the manufacturer to choose the most suitable rope characteristics:
- Purpose of Rope
- Drive Type: drum or sheave
- The design of the rope
- Diameter, length of rope (dimensions and tolerances)
- Material rope
- The core material of the rope
- Sealing rope ends
- The method and direction of lay
- Requirements for impregnation
- Breaking load of rope as a whole, or the total weight of the tensile strength of conventional length m
- Features of the package
- Amount
- Test report
- Remarks
GENERAL INFORMATION
The use of the cable
Steel wire cable is recommended for use in a wide variety of lifting devices, from hand parts to cranes for lifting and moving goods, parts and structural elements. Steel wire cable is part of the majority of lifting mechanisms and devices. Depending on the design, the steel wire has a different coefficient of expansion and flexibility. Steel wire cable is made of carbon steel and galvanized. Technically cables are difficult and responsible view of wire products. They have a large number of types and designs vary in shape and cross-section of both the cable and its elements, as well as physical and mechanical characteristics of the wires and cores.
The design of the cable
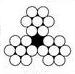
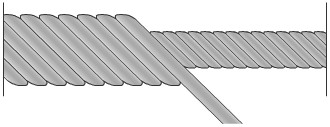
Structurally, the steel wire is made of high-strength wire and core. Wire wraps around the core and get a strand, strands, in turn, also wrap around the core and get the steel cable (see. Fig. 1).
Example for steel cable: 6 х 7 + FC.
- The first number - the number of strands of rope.
- The second - the number of wires in the strands.
- The third - the number of cores including cores in the strands, unless the figures - one in the center of a nonmetallic wire rope, and a steel core strands.
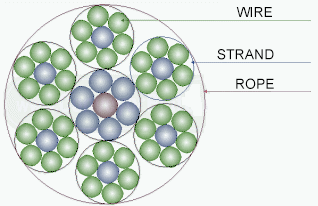
Cable core
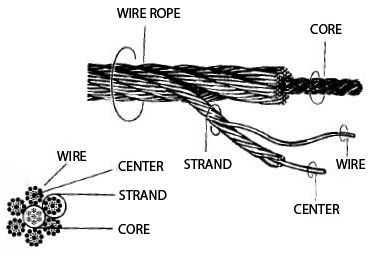
The central core fills a void in the center of the cable and prevents the strands from falling through the center. The metal core is a common strand of wire or steel wire, stranded of several strands; in the first case it is called a full-metal rope, in the second - a special wire rope core. Organic cores, made from hemp, manila, sisal or cotton fabric, contribute to the formation of the round form of a cable and being impregnated with anti-corrosion, antiseptic grease (Vaseline Gun grease, cable ointment, etc.), Protects the inner layers of wire rope from corrosion, reduce friction there between and thus prolong the service life of the cable. Mineral cores are made of asbestos used in cables, designed for operation at high temperatures.
Specifications of cable cross-section
 |  |  |  |  |
| 6х7 GOST GOST 3069-80 | 6x12 DIN 3068 | 6x24 DIN 3068 | 6x30 | 6x19 GOST 3070-88 |
 |  |  |  |  |
| 6xS(19) GOST 3077-80 | 6xW(19) DIN 3059 | 6xFi(21) | 6xFi(25) GOST 7665-80 | 6xWS(26) |
 |  |  |  |  |
| 6x37 GOST 3071-88 | 6xFi(29) | 6xWS(31) | 6xWS(36) GOST 7668-80 | 6xSES(37) |
 |  |  |  |  |
| 6x19+IWRC GOST 14954–80 | 6xS(19)+IWRC GOST 3081-80 | 6xW(19)+IWRC GOST 14954–80 | 6xFi(25)+IWRC GOST 7667-80 | 6xWS(26)+IWRC |
 |  |  |  |  |
| 6x37+IWRC | 6xFi(29)+IWRC | 6xWS(31)+IWRC | 6xWS(36)+IWRC | 6xSES(37)+IWRC |
 |  |  |  |  |
| 6xWS(41)+IWRC | 7x7 GOST 3066-80 | 7x19 TU 14–173–49–2004 | 7x37 | 7xFi(25)+IWRC |
 |  |  |  |  |
| 7xWS(36)+IWRC GOST 7669-80 | 8xS(19) | 8xW(19) | 8xS(19)+IWRC | 8xW(19)+IWRC GOST 14954-80 |
 |  |  |  |  |
| 8xFi(25)+IWRC GOST 7667-80 | 8xWS(31)+IWRC | 17x7 | 18x7 | 19x7 |
 |  |  |  |  |
| 34x7 | 35x7 | 1x37 | 3x7 GOST 3093–80 | 8x7+1x19 |
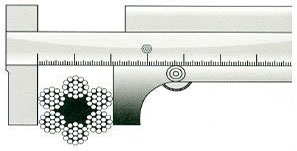
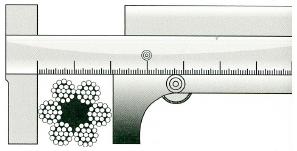
Measurement of the cable diameter
Calculated rope determined by the "nominal diameter". For the measurement of the actual diameter of the caliper is required, the length of the jaws exceeds 3/4 the diameter of the rope. Measurements are carried out in two cross-sections spaced at least 1 m at each point diameter is measured in two mutually perpendicular planes. The new rope arithmetic mean of the four measurements must be within the tolerances specified for the nominal diameter.
The margin of safety rope
Calculate margin for each type of cable is the case enough complicated, due to the fact that this factor depends not only on gravity, but also on the speed of the cable in operation, the type of connector elements at the ends of the cable, by increasing / decreasing the operating speed of the cable , cable length, number, size and location of the hoisting rope pulleys, drums, etc. characteristics of safety cable shown in the table below are the minimum requirements within safe operation and installation.
| Purpose of products | Min. margin of safety |
| For elevators | 10 |
| For cranes, lifting transport cars, slings | 6 |
| For traction winches and towing vehicles | 4 |
| For the cableway, cable cranes | 3 |
Specification and technical characteristics of the cable (without a numerical scale)
| Resistance to abrasion | |
| Crushing strength | |
| Endurance | |
| Safety factor |
The technological process of wire ropes
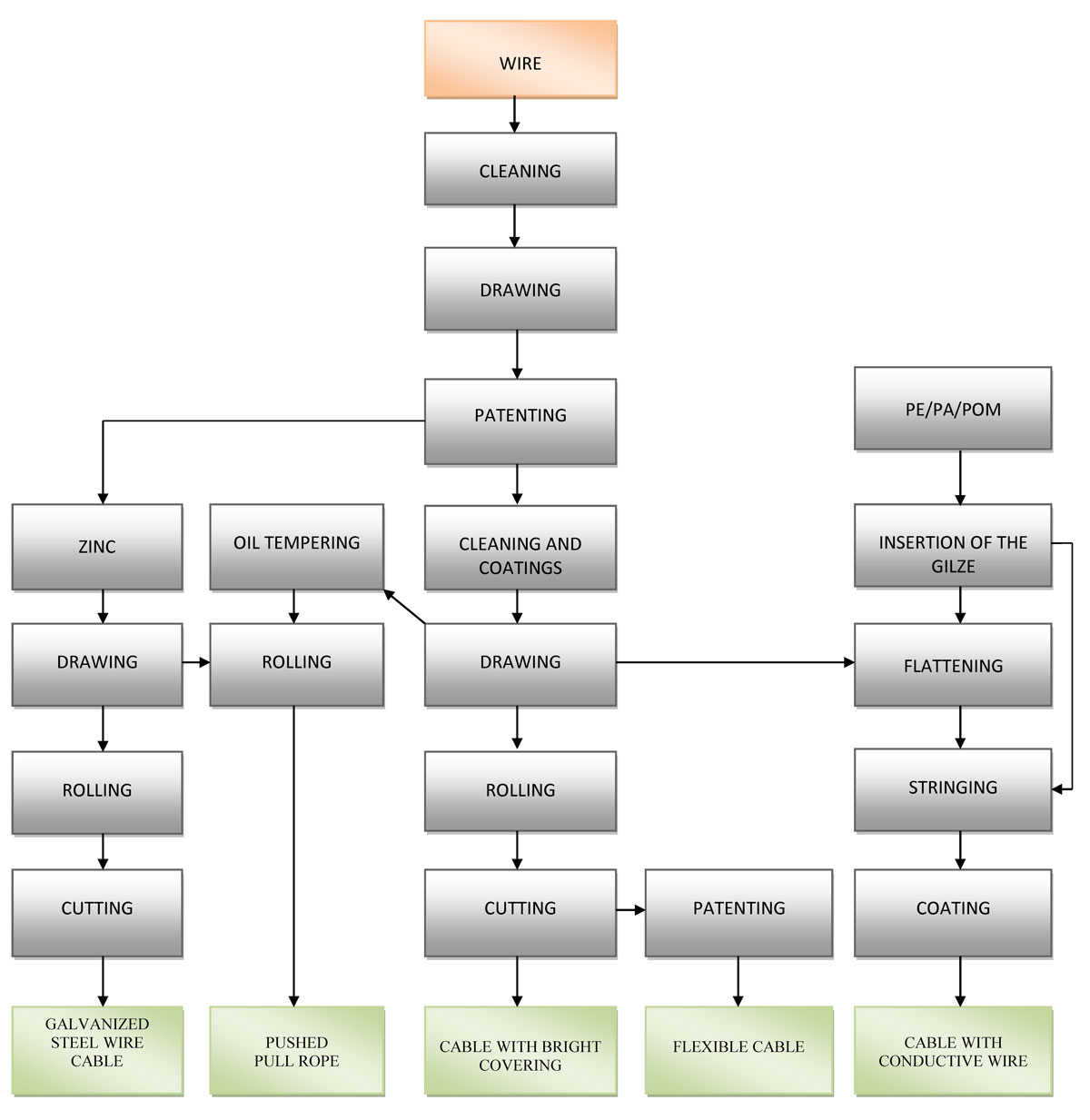
USE, RECOMMENDED FOR STEEL CABLES AND ROPES
| Design | ||||
| A lock | The core | Direction and acombination of lay directions | ||
| Cranes, digger | Jib ropes | 6х19 filler (6х25Fi) | IWRC | O or L |
| 6x36 | IWRC | O or L | ||
| Lifting ropes of tower cranes | 6х19 filler (6х25Fi) | IWRC | O | |
| 6x36 | IWRC | O | ||
| 18x7 | FC or Strand core | O or L | ||
| Ropes with capture | 6x19 | IWRC | O | |
| Tower cranes | Lifting ropes of tower cranes | 18x7, 19x7 | FC or Strand core | O or L |
| Earthmoving and mining machinery | Traction ropes | 6x19 filler (6х25Fi) | IWRC | O |
| Pull ropes канаты | 6x19 filler (6х25Fi) | IWRC | O | |
| Lifting ropes for an inclined lift | 6x19 filler (6х25Fi) | IWRC | O | |
| 6x36 | IWRC | O or L | ||
| Ropes for drilling machine | 6x19 filler (6х25Fi) | IWRC | O | |
| Drilling rigs (rotary) | Ropes for drilling machine | 6x19 filler | IWRC | O |
| Heading ropes | 6х7 galvanized | Poly | O | |
| The cables for the mining industry | 6x19 filler (6х25Fi) | IWRC or FC | O | |
| Rigs (drums) | Ropes for drilling machine | 6х21 filler, left lay | FC | O |
Note to the designations of rope core types:
| ||||
Kinds of steel ropes and cables
1. By design:
- single stranding
– Consisting of one, two, three or more concentric layers of wires, twisted in a spiral; Ropes single lay twisted only round wire, usually called spiral ropes. Spiral ropes in the outer layer having shaped wire ropes are called closed and semi-enclosed structured; on loss of each shaped wire rope is held in adjacent wires. Ropes single stranding intended for later weave into a rope, called strands; - double stranding
– Consist of strands twisted in one or more concentric layers. These cables may be monolayer or multilayer. Multilayer lay has high flexibility and large bearing surfaces, and moreover, can impart rotation-resistant properties of the rope. Double stranding ropes are designed to follow lay, called strands; - triple stranding
– Consisting of a double lay rope (strands) twisted in concentric layer.
.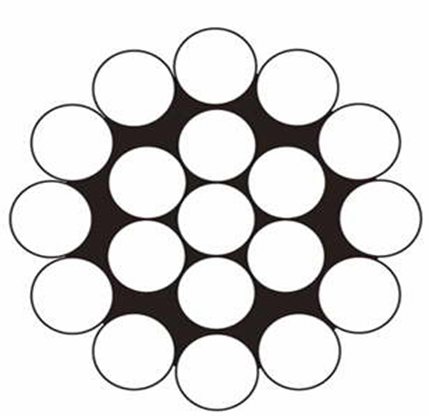 | 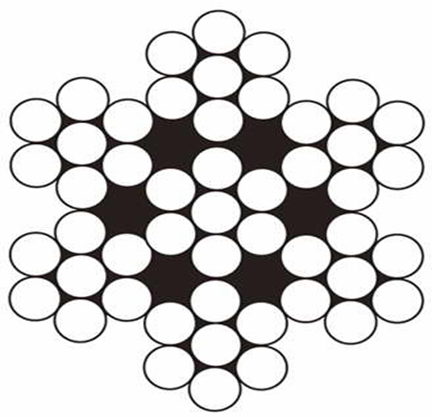 |  |
| Spiral single-stranding rope | Double stranding rope | Triple stranding cable (strands) |
2. According to the type of lay of the strands:
- with the point touching of the wires between the layers - TC
- with linear touch of the wires between the layers - LK
- with linear touch the wires between the layers with the same diameter of the wire strands in layers - LK-G;
- with linear touch the wires between the layers with different diameters of wires in the outer layer of strands - LK-P;
- with linear touch the wires between the layers and filling wires - LK-G;
- with linear touch the wires between the layers and with the strands in layers of wires of different diameters and layers of wires of the same diameter - LK-PO;
- Combined dot-linear touch of the wires - TLC
Strands with point touching the wires are manufactured in several manufacturing operations, the number of which depends on the number of layers of wire. Wire layers have different steps in layers strands and wires between the layers overlap. This arrangement increases the wear at shifts during operation creates significant contact stress, contribute to the development of fatigue cracks in the wire and reduces the duty ratio of the metal section of the rope;
These strands are manufactured in a single technological method, with the permanence of steps lay wires in all layers of the strand is maintained. For linear contact wire and strand diameter is selected depending on the design of the latter. Thus, in the top layer of strands of the rope type LK-0 are used for the same diameter of the wire layers, strands type LK-P in the outer layer have different wire diameters. There is a kind of rope with linear touch of the wires between the layers and having strands in layers with wires as the different and the same diameter-LK-RO. In three layer linear strands touch hold various combinations of the above types of strands. It should be noted that the efficiency of ropes with linear contact wires in the strands when properly selecting the design of the rope is significantly higher than the efficiency of ropes with wires touch point;
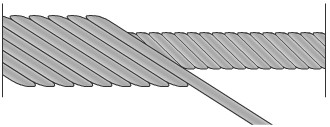 |  |
| Spot touch wires in strands (TC) | Linear contact of wires in strands (LK) |
Strands dot line of contact is obtained by replacing the central wire strands linear touch by 7 wire strand: in this case, on the two-layer type strand LC layer wires of the same diameter with the point touch are laid. The design of these strands allow their manufacture on stranding machines with a relatively small number of bobbins. In addition, the strands of the TLC with an appropriate choice of parameters have increased lay rotation-resistant properties;
3. By cross sectional shape of strands:
- Round-strand;
- Shaped-strand.
4. By degree of rotation:
- rotation
- With the same focus of stranding wires at single-strand ropes; - low-rotation
- Multilayer, multi-stranding and single-stranding from opposite focus of stranding - MK.
5. By core material:
- with a metal core - MS
- Strand - steel single-stranding core rope
- IWRC - steel wire core single-stranding
- with organic core of natural or synthetic materials - OS
- FC - fiber core
- NFC - core from Organic fiber
- SFC - a core of synthetic fiber
- FC(R) - Fiber reinforced core
The metal core is expedient to be applied in cases when it is required to increase the structural strength of the rope when the multilayer coiling it onto a drum, to reduce the structural elongation of the rope under tension, and also during operation of the rope at an elevated temperature. One of the most common designs of this type is a double lay rope from 6-7 wire strands arranged around a central 7-stranding wire. The metal core may be made from conventional soft wire or cable with tensile strength less than 900 N / mm2.
In most designs, to provide the ropes of desired flexibility and elasticity as a core in the center of the rope, and sometimes in the center of the strands used organic lubricant impregnated cores of hemp, manila, sisal or cotton yarn. It is also possible the use of asbestos cord cores and plastic (polyethylene, nylon, nylon etc.);
6. By way of lay:
- nonrotating - H
- On stranding internal voltage at rope is removed straightening and preliminary strain in such manner that after removing dressings from the end of rope strands and wire save specified position. Nonrotating ropes in comparison with rotating have series of advantages: more great flexibility and more uniform distribution tensile efforts on Strands and wire, increased resistance to fatigue stress, lack aspirations upset the straightness at unfolding. - rotating
- Wire strands at this case don’t save its provisions at tightrope after remove dressings from end;
7. By degree of rotation it is possible to distinguish following types of ropes:
- rotation;
- low-rotation - МК
These cables should be distinguished from nonrotating. In low-rotation ropes thanks to the selection of lay directions of the single-stranding wires (in spiral ropes) or strands (multilayer double-stranding), eliminating the rotation of the rope around its axis at a free hanging cargo. A prerequisite of manufacturing low - rotation rope strands is the location of two or three concentric layers with opposite direction of lay of each series of concentric strands. In this case, the torques of all strands of the rope are balanced to prevent the rotation of the total rope around its axis.
8. By the degree of balance:
- planished – Р;
- nonplanished .
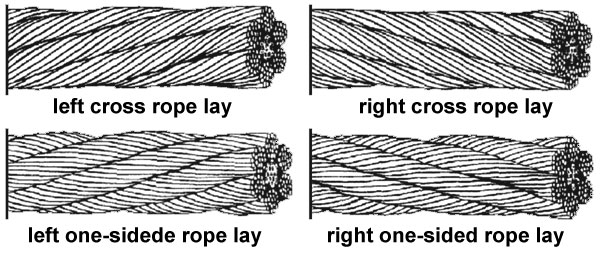
9. By the direction of lay of the rope:
- Right - R;
- Left – L.
10. by combining destinations lay ropes and rope elements in the double and triple stranding:
- sided stranding
- Direction of stranding rope and direction of stranding wire are the same - O. They are less wearing and more bending, but easily untwisted, especially under load; - cross stranding
- With opposite direction of stranding of the wire and of the rope. The ability of unwinding is much less than at the first type ropes; - combined stranding
- With while using at tightrope strands right and Left directions lay. - triple stranding
The direction of strand is set as follows:
- Spiral rope - in the direction of lay of the wires of the outer layer;
- Double lay rope - in the direction of lay of the outer layer of strands in a rope;
- Triple lay rope - in the direction of lay of the strands in the rope.
11. By the mechanical properties of the wire:
- brand general purpose of steel ropes
- VC (High quality), B (high quality), 1 (normal quality). - brand remaining ropes
- B (high quality), 1 (normal quality).
12. By the type of surface coverage of wires in the rope:
- uncoated;
- zinc coated
- For specially Hard aggressive work conditions (OJ);
- For Hard aggressive work conditions (F);
- For medium aggressive work conditions (P);
- With cover rope diameter 3,1-5,0 mm Polyethylene low pressure.
13. By appointment:
- Man shaft - GL (VC brands, B)
- Employees to climb and transportation of people and goods; - Cargo - D
— For the transportation of goods (G). The cargo ropes and wireline are widely used in the tackle and hoists, and other cargo construction equipment.
14. By precision in manufacturing:
- normal;
- increased – Т
- with stricter limit deviations by diameter rope.
15. By the shape of the cross section of rope strands:
- Round-strand
- Their cross-section is close to circle. - Shaped-strand
- Trihedrally -, flat - and oval-strand having much great surface contact with coiling than round-strand and different diversity forms cross section as most rope, so and its elements and also physical - mechanical characteristics of wires and cores. The flat ropes made from strands of alternate - Right and Left - stranding and stitchlocks or rods. Their width at some cases can be up to 250 mm. - twisted round cables have different lay:
- Single spiral (opened, semi- and closed types) ,
- Double from round or shaped (triangular, oval etc.), strands (3 to 8),
- Triple.
They may also be low-rotating (number of strands - 18 to 31 with opposite direction of lay of single layers). The diameter of the rope twisted around is up to 100 mm. The combination of twisted strands of steel rope coated with plastic or hemp yarn. Non-rotating ropes consist of tightly packed groups of spiral steel wire or rope, spiral wound or crimped terminals. Typically, they are collected at the site of application, and their diameter may reach 1.5 mm, and the tensile strength (depending on the diameter) - 1000 N / mm2. Wicker weave ropes made of an even number (usually four) strands, of which one half is the right direction of weaving, and the other - left; its cross section is a square.
LABELING OF ROPES
Each rope must be equipped with a metal label, which states:
- The name or trademark of the manufacturer;
- the number of rope in the numbering system of the manufacturer;
- symbol of rope;
- the length of the rope or of each segment, starting from the neck of the drum, m;
- gross mass in kilograms;
- date of manufacture of the rope.
The label firmly attached in a conspicuous place or cheek drum coil. When winding the rope on the metal drum label can be attached to the end of the rope. Transport marking - GOST 14192-96 for.
Example of ropes symbols
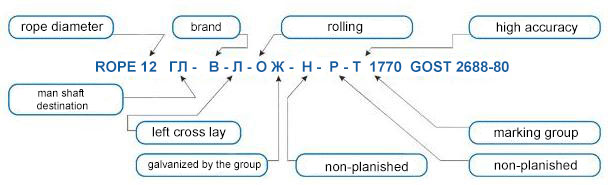
All of the above properties of the rope are reflected in its labeling. For example, labeling cables with a diameter of 15 mm man shaft destination brand VK, galvanized by the group G, low-rotating, left cross lay, increased manufacturing-rotation, high accuracy, marking group 1900 N / mm2 has the following notation:
Rope 15-GL-VK-M-MC-LC-T-1900 GOST (TU)
marking ropes GOST 3079 with a diameter of 25.0 mm, cargo destination, 1 mark, galvanized by the group F, the left-sided lay, non-rotating, non-planished, high accuracy, marking group 1370 N / mm2 (140 kgf / mm2) has the following notation:
Rope 25-G-1-G-L-O-H-T-1370 GOST 3079-80
wireline with a metal core with a diameter of 32 mm, grade B, straight cross lay, increased manufacturing accuracy T, group marking of tensile strength 1570 N / mm2 (16 kg / mm2) is labeled as follows:
Rope MC-32-T-B-1570 GOST 16853-88
STORAGE, INSTALLATION AND MAINTENANCE OF ROPES
Packing
The ropes are wound on wooden drums according to GOST 11127-78 or metal drums, as well as on retracting drums or coils in the prescribed manner.


Drums
The diameter of the neck of the drum must be at least 15 nominal diameter of the rope. Tail of the drum should protrude over the outer layer of the rope wound at least twice the diameter of the rope with a diameter of 25 mm and less than 50 mm when the diameter of the rope more than 25 mm.
Winding several segments of the same size is allowed. The ends of the rope must be fixed. The outer end of the rope is tied with organic core according to GOST 5269-93 or other normative and technical documentation, or wire according to GOST 3282-74 or other normative and technical documentation, or with strand or rope or belt according to GOST 3560-73 and is attached to the inner side of the drum.
Drums with ropes of man shaft destination are lagged with boarding on request, the maximum gap between them should be not more than 50 mm, or wrapped with a rope or polymer belt according to GOST 10354-82 or other normative and technical documentation, or waterproof paper in accordance with GOST 8828-89 or GOST 515 -77.
Coils
The coiled rope must be firmly tied with a soft wire according to GOST 3282-74 or other normative and technical documentation, or a strand of rope or belt according to GOST 3560-73 or other normative and technical documentation, in at least four locations, evenly spaced circumferentially. Packaging ropes being shipped to the Far North and remote areas, as well as ropes, sent by sea, made to GOST 15846-79.
Recommended dimensions of the coils:
- outer diameter – not more than 1200 mm,
- height of the coil – not more than 800 mm,
- inner diameter of the coil must be at least 15 nominal diameter of the rope.
Handling
The main task of handling for the ropes in terms of their operation is to maintain the shape and structure of the rope, giving it the on production, and protection of its mechanical and corrosion damage. This makes compliance with the following basic rules of the storage, installation and use of ropes.
Steel ropes are supplied on wooden drums according to GOST 11127-78 or metal drums on the technical documentation of the plant. It is also allowed to supply cables weighing up to 400 kg in coils with an outer diameter - 1200 mm, coil height - not more than 800 mm, the inner diameter of the coil must be at least 15, nominal diameters of the rope.
The ropes are supplied to the Far North, as well as ropes, which provided transportation by sea, packed in accordance with the requirements of GOST 15846-79 . Products to the areas of the Far North and remote areas. Packing, marking, transportation and storage.
Storage ropes by the storage group conditions G2 GOST 15150-69
When storing rope wound on the drum, the axis of the drum must be parallel to the floor on which the drum is attached. Received deposited ropes are subject to immediate inspection and lubrication grease bare cable during transportation, loading and unloading areas of rope. For prolonged storage the ropes should periodically, at least every 6 months inspected at the outer layer of the cable and lubricated with grease.
If you want to test the rope dense rail end of the rope should be performed in accordance with p. 2.10 of GOST 3241-80. Rope segment made with a mechanical saw blade. Ropes with metal core and ropes of closed design can be cut with help of electric welding simultanious welding of the end of the rope.
Installation
The basic requirement when installing the rope is to protect it from unwinding. It is necessary: set the rope drum on unwinding device so that the drum axis is horizontal. The end of the rope must go above or below the drum, which is in the process of winding the rope has to be braked. The distance between the drums must be at least 300 rope diameters. During installation, the rope should undergo a minimum number of bends, especially alternating.
Unwinding the rope out of the coil
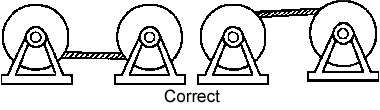
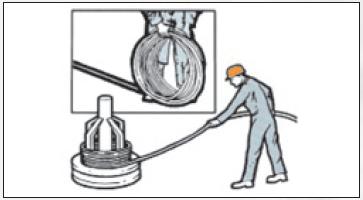
Put the coil on the ground and unwind the rope smoothly, in a straight line, taking care to avoid contamination with soil / metal grit, moisture and other harmful substances (Fig. 1). Coil can be put on the rotary uncoiler and pull the outer end of the rope, turning the coil.
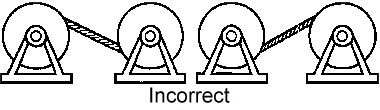
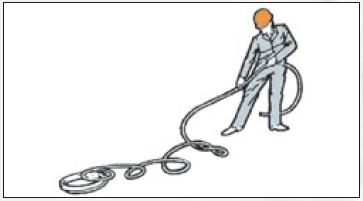
Do not unwind the rope with a fixed coil, as this can lead to rope twist and formation of loops that will significantly reduce the performance of the rope (Fig. 2).
Installation of rope from the drum
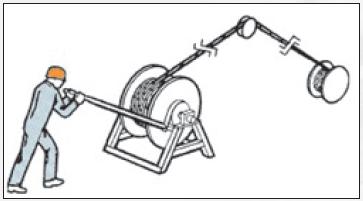
Pass the coil through the axial hole of the drum and put it on a support that allows the drum to rotate and to brake its rotation in order to avoid crowding the rope. When multilayer coiling drum must be placed on the device, which will enable the return line tension during its transport from the winding drum to the drum of the elevator installation. This will help make sure that the lower coils densely wound on the drum (Figure 3).
The angle of deviation should not exceed 1.5° in the case of a smooth drum and 2,5° using a drum with a screw thread, to ensure a minimum lateral rope wear by friction of the adjacent coil in case of a smooth drum, and side surface cut grooves in the case of a drum with a screw thread.
Recommended ways of rope rewinding
Regular lubrication of ropes during operation greatly increases their service lifes. Lubrication of rope prevents corrosion and reduces wear on the units and the drum. Ropes coated with a lubricant during manufacture of the whole section, as in the process of operation - a continuous solid film of 0.1 mm thickness. As lubricants Torsiol-55, GOST 20458-75, Torsiol 35, BOZ-1 are used for technical documentation. The temperature of the lubricant in its application to the rope should be 80-100°C. Rope is purified before applying the lubricant from the old grease and dirt in different ways. The simplest of them - clean with steel brush.
RECOMMENDATIONS FOR USE ROPES OF DIFFERENT STRUCTURES
Ropes single-stranding of round wires
have an increased stiffness, therefore recommended for use in conditions where there is no alternating bending and tensile loads prevail (reinforcing, lightning cables, ropes for overhead power lines, fences, braces, shrouds, etc.).
Ropes with strands of TK type
is not recommended for critical and intensive lifting equipment. They are used in conditions where pulsating and alternating bending loads are insignificant or completely absent (bracing, temporary logging fasteners, etc.)
Ropes with strands of LK-O type
has an increased corrosion resistance, work in conditions of abrasion due to the presence in the upper layer of wires of larger diameter. These cables are widely spread as lifting on vessels and elevators, brake - on mine hoisting installations, traction - on a rope course, cable cranes, etc. However, for the normal operation of these ropes requires a slightly increased diameter of blocks and drums.
Ropes eight-strand of LK-O type
Ropes are designed for a variety of lifting mechanisms that require increased flexibility and resistance to surface wear wires.
LK-P Ropes
Ropes with strands of LK-P type have increased degree of filling the cross section of the metal and therefore have found use in a variety of lifting devices with high axial loads. Especially because of the presence, in the outer layer, the small-diameter wires. Cables can be operated in a hostile environment.
Ropes triple stranding of LK-R type
Have increased flexibility. Improved structural density can increase their strength, they can be used in construction and metallurgical cranes, mine hoist, excavators, cable cranes, etc.
Ropes of LC-R O type
Ropes of LC-RO type are relatively large number of wires in the strands and therefore have greater flexibility. The presence in the outer layer of relatively thick wire ropes to successfully apply them in terms of abrasion and corrosion.
Ropes triple stranding
Characterized by high structural stability, a large duty cycle, and a large supporting surface. They are used in a large high-end loads and abrasive wear. Is used as a head-on hoist with pulleys friction and multi-layer coiling on a drum of winch.
Ropes of closed structures
Applied as a carrier in the lift cable cars and cable cranes. Big filling factor of the metal cross-section of the rope, the maximum footprint, minimal elastic and permanent elongation during operation, the ability of shaped wires to maintain their position in the rope at breakage, considerable height of the outer shaped wires cause widespread use of ropes of closed structures in the mine and mining industry As conductor and demolition. Ropes of closed construction made of zinc-coated wires are widely used in the construction of various civil engineering structures (suspension bridges, overpasses, antenna mast structures, etc.) as load-bearing elements.
Ropes with strands of LK-G type
Ropes of LK-G type along with increased flexibility are highly durable. They have been used in almost all industries in the materials handling installations. However, they should not be exposed to corrosive environment, due to the presence in the construction of thin wire rope required.
Ropes with strands of TLC type
Have an increased number of layers of wires in a strand, and as a consequence have high flexibility property. Are used in various lifting systems with a large multiplicity of reeving system. They are used as head ropes on vertical hoisting.
Ropes reinforced
Steel ropes for reinforcement of concrete building structures used as prestressed reinforcement of prestressed concrete structures.
Ropes of combining materials
Ropes are used for the construction of fishing gear and rigging. Have greater flexibility and strength as compared with the ropes of polymeric material.
Wires uninsulated
Wires used for the transmission of electric energy in air electric networks.